Backup (.bak) Files
Drawing backup files are typically created every time a .dwg file is manually saved. By default the file will be saved in the same location as the .dwg and will have the same name as the drawing but with a .bak extension, such as, site_topo.bak. A backup file is an exact copy of the drawing file prior to the last save. As such, backup files are always one version older than the currently saved drawing. Only one backup file is retained at a time so newly created backups will always replace older backups of the same name.
Note: Backup files are created only if the system variable ISAVEBACK is set to 1.
Backup files are essentially renamed .dwg files. Data saved in .bak files can be recovered by renaming the .bak extension to .dwg and then opening that file in AutoCAD.
MOVEBAK Command
Included in the AutoCAD Express Tools is the MOVEBAK command which permits specifying an alternative folder for the bak files when created. To keep bak files in a single location—as opposed to keeping them in the same folder as the associated drawings—use the MOVEBAK command to specify another folder and all bak files will be automatically moved there when created. Enter "." as a value in the command to reset AutoCAD to the default behavior.
Note: MOVEBAK is only available in Autodesk products that include the AutoCAD Express Tools. The MOVEBAK command has not been updated in recent years so it may not support paths with embedded spaces.
Automatic Save (.sv$) Files
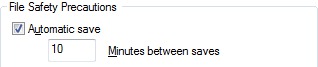
Automatic save files—commonly referred to as "autosave" files—are backup files created automatically by the Autosave feature. Automatic save is enabled by default and the number of minutes between automatic saves can be set in the Open and Save tab in the Options dialog box or by using the SAVETIME system variable. Automatic saves are only done if a drawing has been modified after the last save. An automatic save will not save to the current drawing. Instead, a temporary file with the extension .sv$ is generated. QSAVE, SAVE, and SAVEAS will delete the current .sv$ file and halt the automatic save timer until an edit is made to the drawing.
If AutoCAD crashes or is otherwise abnormally terminated during a session, data saved in .sv$ files can be recovered by locating the autosave file, renaming the .sv$ extension to .dwg and then opening that file in AutoCAD. The autosave file will contain all drawing information as of the last time autosave ran. When AutoCAD closes normally, .sv$ files are deleted as any open drawings would be closed/saved normally.
The location of autosave files in the Windows operating system can be determined by going to the Files tab in the Options dialog box and inspecting the Automatic Save File Location folder in the hierarchy, or by using the SAVEFILEPATH variable. In the Mac OS, this can be found under the Application tab in Preferences.
By default in Windows, the location is taken from the TEMP environment variable in the operating system. An easy way to open the user Temp folder is to type %tmp% in the Start menu search or in the location bar of any folder window. In the Mac OS, the default location is in the user's folder within /Documents/Autodesk/Autosave.
Automatic save can be disabled by unchecking Automatic save in the Open and Save tab in the Options dialog box or by setting the SAVETIME system variable to 0. Disabling automatic save prevents AutoCAD from automatically creating sv$ files while working. In the event of a crash, there will be no interim files to use for data recovery.
Tip: The TIME command is useful in tracking whether an automatic save file will be created because it gives information about the countdown time and whether modifications have been made to the drawing.
Temporary (.ac$) Files
By default, temporary files have an .ac$ extension. These files contain information that is used by various AutoCAD commands (such as UNDO) and do not contain any drawing data that can be recovered. They should only exist during an AutoCAD session but may be left behind if AutoCAD crashes or is abnormally terminated.
Drawing Recovery Manager
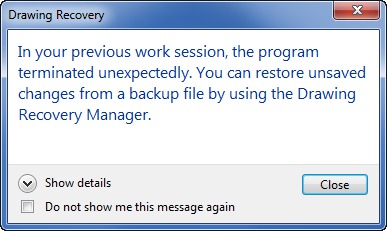
Originally introduced in AutoCAD 2006, the Drawing Recovery Manager (DRAWINGRECOVERY) helps with the task of locating and opening drawings that were last open when AutoCAD crashed, as well as any backup and autosave files associated with those drawings.
When launching AutoCAD after a crash, the Drawing Recovery Manager determines what drawings were active when the crash occurred and displays those drawings, and the associated backup and autosave files, in a single interface.
The Drawing Recovery Manager can open backup and autosave files directly into the current session of AutoCAD without having to manually locate and rename those files. The first time a saved backup or autosave file is opened from the Drawing Recovery Manager, a prompt to rename the file will be shown.
Note: The Drawing Recovery Manager is only useful after a crash has occurred and will only display information about drawing files that were active during a session that crashed. The Drawing Recovery Manager cannot be launched during a normal working session to show the backup and autosave files for the current drawing.
Tip: On the Mac OS, drawings or recovered files after a crash can be locked and need to be unlocked in the Finder using Get Info and disabling the Locked checkbox.