Construction Lines
Autocad Tutorials from beginner basics to advanced techniques.

 . Find
. Find


 . Alternatively, you can click
. Alternatively, you can click | If you want to… | Then… |
|---|---|
| specify a different layer standard on which to base the layer key style | select a new layer standard for Standard. |
| specify that the layer key style is not based on a layer standard | select Non Standard for Standard. |
| If you want to… | Then… |
|---|---|
| modify the description for a layer key | double-click the text that you want to change for Description, and enter new text. |
| modify the layer name | under Layer, click the [...] button. Specify the appropriate values for layer fields, and click OK. |
| modify the color for a layer key | under Color, click the current value. Select a new color, and click OK. |
| modify the linetype for a layer key | under Linetype, click the current value. Select a new linetype, and click OK. |
| modify the lineweight for a layer key | under Lineweight, click the current value. Select a new lineweight, and click OK. |
| specify whether a layer key will plot | under Plot, click the printer icon to turn plotting on or off. |
| specify whether to allow layer field overrides | under Allow Overrides, clear the options for which overrides are not allowed.
Tip: When you first add a new layer key by default the name generated for the layer is not yet based on the layer standard used. This is why the layer overrides are inactive. Modify first the layer name associated to the key by clicking the [...] button. Once the name is based on the layer standard, you can allow overrides to the standard.
|
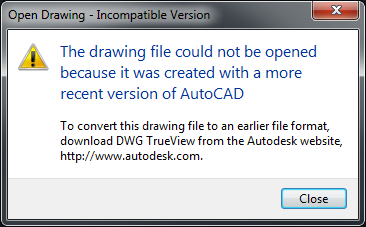
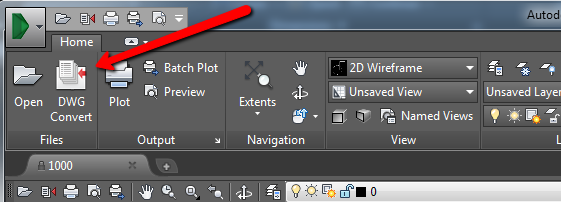

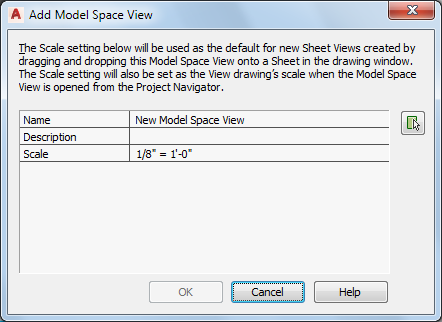
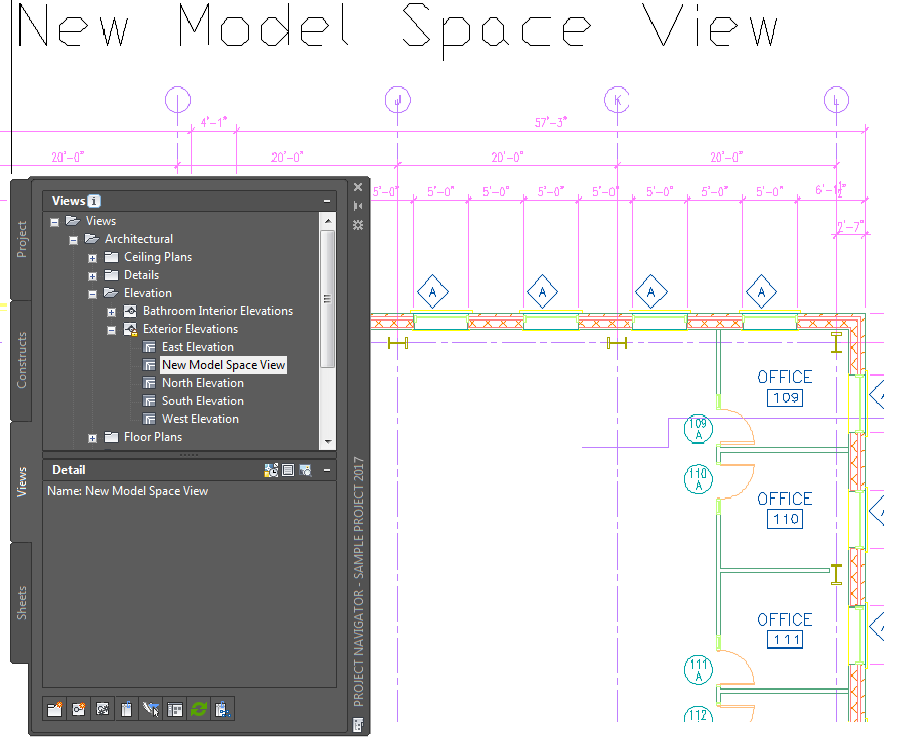

| If you want to… | Then… |
|---|---|
| enter a description for the model space view | click the setting for Description and add a description of the model space view. |
| change the scale of the model space view | select a scale from the list of those used in the current view drawing. |
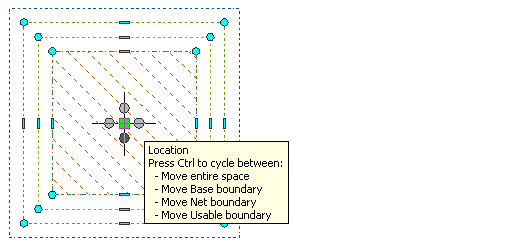
| If you want to… | Then… |
|---|---|
| move the entire space | move space to the desired location and click to release it. |
| move the base boundary of the space | click and hold the location grip, and press Ctrl to switch to Move base boundary mode. Then move the base boundary to the desired location, and click to release it. |
| move the net boundary of the space | click and hold the location grip, and press Ctrl twice to switch to Move net boundary mode. Then move the net boundary to the desired location, and click to release it. |
| move the usable boundary of the space | click and hold the location grip, and press Ctrl 3 times to switch to Move usable boundary mode. Then move the usable boundary to the desired location, and click to release it. |
| move the gross boundary of the space | click and hold the location grip, and press Ctrl 4 times to switch to Move gross boundary mode. Then move the gross boundary to the desired location, and click to release it. |