Modifying the Properties of 3D Objects
Modify 3D objects by changing their settings in the Properties palette.
3D solids, surfaces, and meshes, and their subobjects can be modified in the Properties palette.
Modify 3D Solid Objects by Changing Properties
By changing settings in the Properties palette, you can modify basic size, height, and shape characteristics of primitive solids. For example, to change a four-sided pyramid that ends in a point to an eight-sided pyramid that ends in a planar surface (pyramid frustum), update the Top Radius and Sides properties.
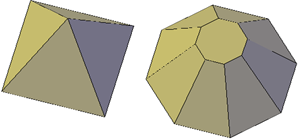
With 3D solids that have been recombined to form compound objects, you can choose to retain the history subobject, which represents components that have been removed. The Properties palette controls the availability and display of these histories.
Modify Surface Objects by Changing Properties
Surface objects have additional properties that are not found in 3D solid or mesh objects. The properties differ depending on the type of surface (NURBS, blend, patch, network, offset, fillet, chamfer, extend, loft, extrude, sweep, planar, or revolve).
Surfaces include the following information in the Properties palette:
- Geometry. Contains information such as radius for fillet surfaces, offset distance for offset surfaces, and taper angle for extruded surfaces. You can also enter mathematical expressions to control some of these properties.
- Maintain Associativity. Toggles associativity for the selected surface.
- Show Associativity. Toggles dependency highlighting if the surface is associated with other surfaces.
- Edge Continuity and Bulge Magnitude. Displays for surfaces that join other surfaces.
- Wireframe Display and U/V Isolines. Turns the wireframe and U/V Isoline display on and off (for non-NURBS surfaces).
- CV Hull Display and U/V Isoparms. Turns the CV Hull and U/V Isoparm display on and off (for NURBS surfaces).
- Trims. Reports whether the surface has any trimmed areas and on which edges.
Modify Mesh Objects by Changing Properties
Mesh objects have additional properties that control the level of smoothness and creases. Crease properties of face, edge, and vertex subobjects are also reflected in the Properties palette.
- Level of Smoothness. Smooths or sharpens the edges of a mesh object.

- Crease Type. Specifies the presence of a crease (or sharpened edge) and the effect of smoothing. Smoothing does not affect a crease with a value of Always. A crease set to By Level retains its sharpness until the mesh object is smoothed to the specified crease level.

- Crease Level. When a crease is set to By Level, indicates the smoothing level at which the crease starts to lose its sharpness.

Modify 3D Subobject Properties
In addition to solids, surfaces, and meshes, you can also use the Properties palette to modify the properties of individual subobjects, such as faces, edges, and vertices. Different properties are available for different types of subobjects.
In some cases, the application of properties can differ depending on the object type. For example, you can modify the properties of mesh faces, including their color. However, the color appearance of a mesh face might differ from the equivalent color on a 3D solid face. This difference occurs because changing the color of a face modifies the diffuse color of the face, but not the ambient color (which is derived from the mesh material property). To obtain a closer match between the color of 3D solid and mesh faces, you can add lights and turn off the default lighting (which disables ambient lighting). You can also try assigning a material that has the same ambient and diffuse color.

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home